1.ls
1.1代码讲解
- 打开文件获得一个文件指针
- readdir()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
#include <stdio.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
void do_ls(char []);
int main(int ac,char *av[]){
if (ac == 1)
do_ls(".");
else
while ( -- ac){
printf("%s:\n",*++av);
do_ls(*av);
}
return 0;
}
void do_ls(char dirname[]){
DIR *dir_ptr;
struct dirent *direntp;
if (((dir_ptr = opendir(dirname))) == NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"ls cannot open %s\n",dirname);
} else{
while ((direntp = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL){
printf("%s\n",direntp->d_name);
}
closedir(dir_ptr);
}
}
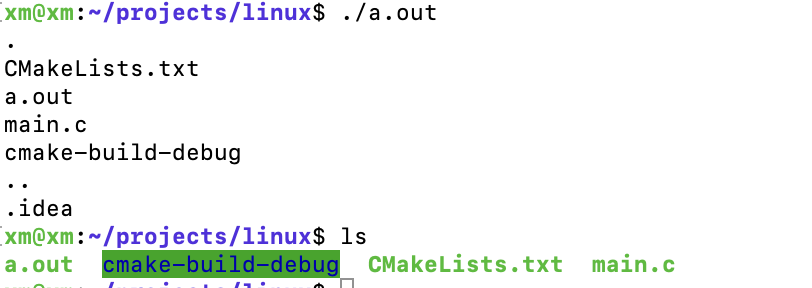
1.2 运行结果对比
1.3 问题改进
- 排序 用数组加sort
- 分栏 格式化输出
- 隐藏文件
- 选项 -l
2. 编写ls -l

- 模式字段
- 连接数 该文件被应用的次数
- 文件的所有者
- 文件所在的组别
- 大小 目录大小都为4096
- 最后的修改实践
- 文件名
2.1 使用stat()函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
int main(int ac,char *av[]){
struct stat info;
stat("./a.out",&info);
printf("模式:%s\n",info.st_mode);
printf("链接数:%s\n",info.st_nlink);
printf("用户id:%s\n",info.st_uid);
return 0;
}
stat 数据结构中基本包含了上述的所有字段。

2.2 实现
上述实现已经非常接近了,最后需要更改几个地方。
mode 将数字权限转为
rwerwerwe,9位分别是,文件所有者,同组用户,其他用户。 r w e 权限分别对应: 4 2 1通过掩码技术获得对应位置权限,文件类型等。详见p77。
根据用户uid 显示用户名
时间处理 , 同who,ctime()实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
#include <stdio.h> // 输入输出
#include <dirent.h> // DIR
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <pwd.h> // pwd
#include <grp.h>
void do_ls(char[]);
void do_stat(char *);
void show_file_info(char *,struct stat*);
void mode_to_letters( int , char [] );
char *uid_to_name( uid_t );
char *gid_to_name( gid_t );
int main(int ac, char *av[]){
ac = 1;
if (ac == 1){
do_ls(".");
} else{
while ( -- ac){
printf("%s:\n",*++av);
do_ls(*av);
}
}
return 0;
}
void do_ls(char dirname[]){
DIR *dir_ptr;
struct dirent *dirent;
if((dir_ptr = opendir(dirname)) == NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"ls:cannot open %s\n",dirname);
} else{
while ( (dirent = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL){
do_stat(dirent->d_name);
}
}
}
void do_stat(char *filename){
struct stat info;
if (stat(filename,&info) == -1){
perror(filename);
} else{
show_file_info(filename,&info);
}
}
void show_file_info(char *filename,struct stat *info_p){
char modestr[11];
mode_to_letters(info_p->st_mode,modestr);
/**
* 这一段的字符串输出格式可以看看
*/
printf("%s",modestr); // mode
printf("%4d ",info_p->st_nlink) ; // 链接数
printf("%-6s", uid_to_name(info_p->st_uid)) ; // u id
printf("%-6s", gid_to_name( info_p->st_gid)) ; // g id
printf("%-12d ",info_p->st_size) ; // size
printf("%.12s ",4+ ctime( &info_p->st_mtim) ) ; // time
printf("%s\n",filename) ; // file name
// printf("\n");
}
void mode_to_letters(int mode,char str[]){
strcpy(str,"----------");
/**
* is directory?
*/
if(S_ISDIR(mode)) str[0] = 'd';
if(S_ISDIR(mode)) str[0] = 'c';
if(S_ISDIR(mode)) str[0] = 'b';
if ( S_ISDIR(mode) ) str[0] = 'd'; /* directory? */
if ( S_ISCHR(mode) ) str[0] = 'c'; /* char devices */
if ( S_ISBLK(mode) ) str[0] = 'b'; /* block device */
if ( mode & S_IRUSR ) str[1] = 'r'; /* 3 bits for user */
if ( mode & S_IWUSR ) str[2] = 'w';
if ( mode & S_IXUSR ) str[3] = 'x';
if ( mode & S_IRGRP ) str[4] = 'r'; /* 3 bits for group */
if ( mode & S_IWGRP ) str[5] = 'w';
if ( mode & S_IXGRP ) str[6] = 'x';
if ( mode & S_IROTH ) str[7] = 'r'; /* 3 bits for other */
if ( mode & S_IWOTH ) str[8] = 'w';
if ( mode & S_IXOTH ) str[9] = 'x';
}
char *uid_to_name(uid_t uid){
struct passwd *getpwuid(), *pw_ptr;
pw_ptr = getpwuid(uid);
return pw_ptr->pw_name;
}
char *gid_to_name(gid_t gid){
struct group *getgrgid(),*grp_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
grp_ptr = getgrgid(gid);
return grp_ptr->gr_name;
}
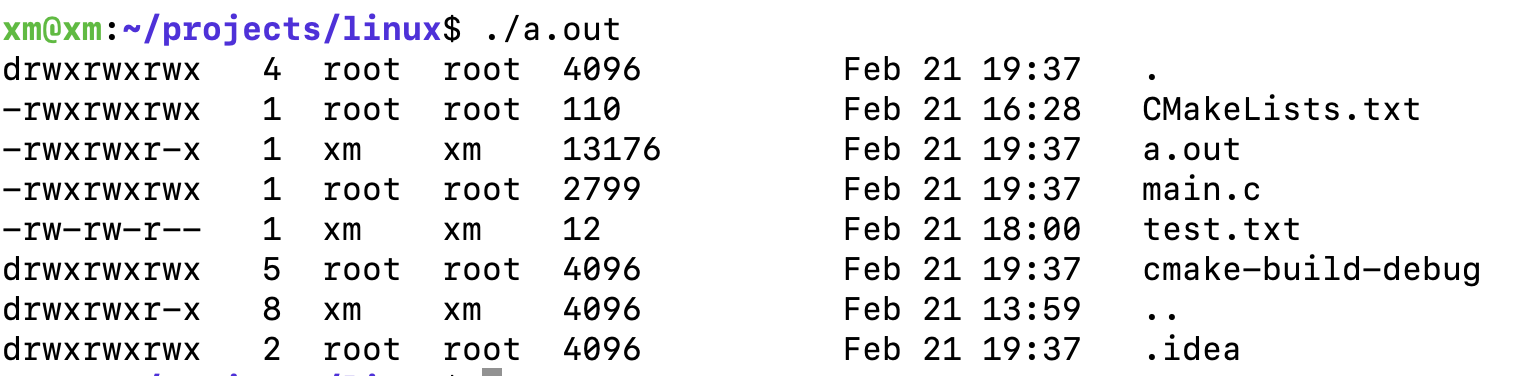
效果图
3. stat st_mode位详解
3.1 st_mode
a.txt : 33188 二进制转换: 100,0000,110,100,100 对应权限位: -rw-r–r–
0000: 作为文件类型 100: 文件特殊属性位 下文详解
3.2 set_user_id 位
先引出问题: 如何更改用户密码文件? passwd命令位于usr/bin/passwd 中,其所有者属于root用户,只有root用户有权限执行改文件。set_usr_id位告诉内核,运行该程序的时候,认为是文件的所有者在运行该程序
- 是否可以更改其他用户的密码?
不能,passwd命令,通过getuid()获得用户id,只能更改对应id的密码。
- 其他的使用场景
比如,游戏把最好成绩给记录下来,记录程序的所有者是DBS,
3.3 set_group_id
同上,略
3.4 sticky 位
交换空间swap 内存换入换出用,现在已经不怎么用了。
4. Unix 文件类型
- 文件分类
普通文件,设备文件,目录文件等。
文件一旦创建,类型无法修改
- umask
umask(022) 是一个系统级变量。(8进制)
比如,在创建一个新文件,不希望同组和其他用户有对改文件的更改权限,即—-w–w–权限关闭,可用八进制umask掩码(全局变量)
