1. 11 个阶段 = 流水线的 11 个楼层
HTTP 框架将请求处理过程分为 11 个阶段,每个阶段可挂多个模块的处理函数。
| 楼层(阶段) | 工作任务 | 默认工人(内置模块) | 你可以加的自定义工人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1楼 | 刚收到请求,检查包裹 | realip 模块 | 「签名验证工人」 |
| 2楼 | 修改快递地址(URL重写) | rewrite 模块 | 「自动补全地址工人」 |
| 3楼 | 分配车间(匹配 location) | Nginx 核心 | ❌ 不允许加人(老板亲自处理) |
| 4楼 | 再次修改地址(location重写) | rewrite 模块 | 「智能地址转换工人」 |
| … | … | … | … |
| 9楼 | 生成包裹内容 | proxy/static 模块 | 「自动打包机器人」 |
| 11楼 | 登记发货记录 | log 模块 | 「大数据分析工人」 |
2. 自定义模块如何「入职」这个工厂?
你需要做三件事:
(1)填写入职申请表(定义模块)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ngx_module_t ngx_http_mymodule = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_mymodule_ctx, // 模块技能描述
ngx_http_mymodule_commands, // 模块能接受的指令
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, // 声明这是HTTP模块
NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL,
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
(2)选择工作楼层(注册到阶段)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 注册到9楼:CONTENT_PHASE
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mymodule_init(ngx_conf_t *cf) {
ngx_http_handler_pt *h = ngx_array_push(
&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE].handlers
);
*h = ngx_http_mymodule_handler; // 工作函数
return NGX_OK;
}
(3)定义工作内容(处理函数)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mymodule_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) {
ngx_buf_t *b = ngx_create_temp_buf(r->pool, 1024);
ngx_sprintf(b->pos, "Hello, this is my module!");
b->last = b->pos + ngx_strlen("Hello, this is my module!");
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = b->last - b->pos;
ngx_http_send_header(r);
ngx_http_output_filter(r, b);
return NGX_OK;
}
3. 实际案例:开发一个「请求头检查模块」
✅ 需求:
- 在请求刚到达时(1楼 POST_READ_PHASE)
- 检查是否存在
X-Auth-Token请求头 - 没有则直接返回 401
✅ 代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
// 1. 定义处理函数
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_check_token_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) {
ngx_table_elt_t *token = r->headers_in.headers.part.elts;
for (ngx_uint_t i = 0; i < r->headers_in.headers.part.nelts; i++) {
if (ngx_strcmp(token[i].key.data, "X-Auth-Token") == 0) {
return NGX_OK; // 有 token,放行
}
}
// 无 token,拒绝
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED;
ngx_http_send_header(r);
return NGX_HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED;
}
// 2. 注册到 POST_READ_PHASE
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_check_token_init(ngx_conf_t *cf) {
ngx_http_handler_pt *h = ngx_array_push(
&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE].handlers
);
*h = ngx_http_check_token_handler;
return NGX_OK;
}
4. 关键总结
- ✅ 阶段是固定的:就像工厂楼层,Nginx 已经建好,不能改
- ✅ 模块是灵活的:你可以在任意阶段插入逻辑(除非禁止)
- ✅ 同一阶段的模块执行顺序:按配置加载顺序运行
- ✅ 可通过
postconfiguration控制优先级
🚀 常用阶段推荐:
| 目标 | 使用阶段 |
|---|---|
| 拦截请求 | POST_READ_PHASE、PREACCESS_PHASE |
| 修改 URI | SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE、REWRITE_PHASE |
| 生成内容响应 | CONTENT_PHASE |
| 请求日志处理 | LOG_PHASE |
通过这种设计,Nginx 保持了核心流程的稳定,又通过模块机制实现了极致的可扩展性,就像“在精确位置插积木”一样加逻辑!
5. 举例说明
本文展示如何将一个自定义模块注册到 Nginx 的 CONTENT_PHASE(内容生成阶段),并拦截请求,返回自定义内容。
1. 模块结构定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#include <ngx_http.h>
// 模块的处理函数(核心逻辑)
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_myhandler(ngx_http_request_t *r);
// 模块的指令定义(可以通过 nginx.conf 配置)
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_mycommands[] = {
{ ngx_string("my_module"), // 指令名
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_NOARGS, // 指令适用范围
ngx_http_myhandler, // 指令对应的函数
0,
0,
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
// 模块上下文结构
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_mymodule_ctx = {
NULL, // preconfiguration
NULL, // postconfiguration
NULL, // create main conf
NULL, // init main conf
NULL, // create server conf
NULL, // merge server conf
NULL, // create location conf
NULL // merge location conf
};
// 模块定义
ngx_module_t ngx_http_mymodule = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_mymodule_ctx,
ngx_http_mycommands,
NGX_HTTP_MODULE,
NULL, // init master
ngx_http_mymodule_init, // init module(注册阶段用)
NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL,
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
2. 实现处理函数逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// 内容生成处理函数(返回固定文本)
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_myhandler(ngx_http_request_t *r) {
// 设置响应头
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_type.len = sizeof("text/plain") - 1;
r->headers_out.content_type.data = (u_char *) "text/plain";
// 构造响应内容
ngx_buf_t *b = ngx_create_temp_buf(r->pool, 128);
ngx_sprintf(b->pos, "Hello, this is my custom module!");
b->last = b->pos + ngx_strlen("Hello, this is my custom module!");
// 输出响应
r->headers_out.content_length_n = b->last - b->pos;
ngx_http_send_header(r);
ngx_http_output_filter(r, b);
return NGX_OK;
}
3. 注册模块到 CONTENT_PHASE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// 模块初始化函数,在 nginx 启动时被调用
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mymodule_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle) {
ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf;
// 获取 HTTP 核心配置结构体
cmcf = ngx_http_cycle_get_module_main_conf(cycle, ngx_http_core_module);
if (cmcf == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
// 注册处理函数到 CONTENT_PHASE
ngx_http_handler_pt *h = ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE].handlers);
if (h == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
*h = ngx_http_myhandler;
return NGX_OK;
}
4. Nginx 配置使用方法
在 nginx.conf 中配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
http {
server {
listen 80;
location /test {
my_module; # 激活模块
}
}
}
访问 http://localhost/test 时,返回内容应为:
1
Hello, this is my custom module!
6. Nginx 处理阶段的完整执行顺序(含自定义模块)
你的疑问核心在于 location 匹配、my_module 触发、11 个阶段的执行顺序。以下是彻底清晰的解析:
1. 完整流程图示
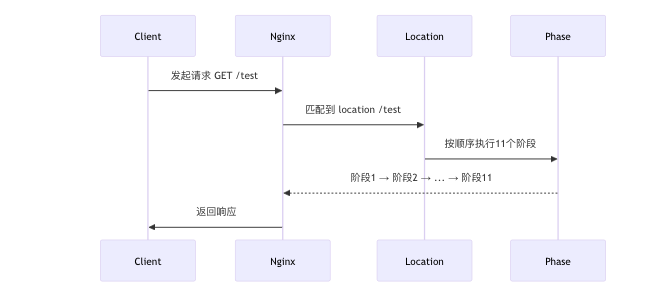
2. 关键顺序详解
(1)先匹配 location,再执行阶段
- location 匹配:
Nginx 首先根据请求的 URI 找到匹配的 location 块(如location /test { ... })。 - 阶段执行:
匹配到 location 后,按照 11 个阶段的固定顺序依次执行,与 location 中指令的顺序无关。
(2)my_module 的触发时机
假设你的配置如下:
1
2
3
4
location /test {
my_module; # 自定义指令
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
- my_module 的作用:
它只是一个指令,用于告诉 Nginx:“在这个 location 中激活我的模块逻辑”。 - 实际执行:
由模块注册的阶段决定(例如注册到 CONTENT_PHASE)。
(3)阶段执行的本质
模块在阶段中的位置:
每个阶段(如 CONTENT_PHASE)可能包含多个模块的处理函数,按模块加载顺序执行。例如:
1 2 3 4 5
// 模块A注册到 CONTENT_PHASE ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE].handlers, &module_a_handler); // 模块B也注册到 CONTENT_PHASE ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE].handlers, &module_b_handler);
执行顺序:
先执行module_a_handler,再执行module_b_handler。
3. 完整案例演示
场景
用户访问 GET /hello,匹配到以下 location:
1
2
3
4
location /hello {
my_module; # 自定义模块指令
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
执行步骤
- 匹配 location
Nginx 发现 URI/hello匹配到 location /hello,读取其中的指令(my_module 和 proxy_pass)。 - 按阶段顺序执行
- 阶段1-8:跳过未注册模块的阶段。
- 阶段9(CONTENT_PHASE):
先执行 my_module 的处理函数(如果它注册在此阶段)。
再执行 proxy_pass 的处理函数(内置的 ngx_http_proxy_module)。 - 阶段11(LOG_PHASE):记录访问日志。
- 响应生成
- 如果 my_module 返回 NGX_OK,继续执行 proxy_pass。
- 如果 my_module 返回 NGX_DECLINED,跳过 proxy_pass。
4. 关键结论
- location 是入口:决定哪些指令和模块会被激活。
- 阶段是固定的流水线:无论 location 里写了什么指令,都按 11 个阶段的顺序执行。
- 模块的执行顺序:
- 同一阶段内,按模块加载顺序执行(可通过调整模块编译顺序控制)。
- 不同阶段按数字顺序执行(1 → 2 → … → 11)。
5. 类比解释
把 Nginx 想象成一个 快递分拣中心:
- location:像是一个分拣规则(例如“所有上海的快件送到A区”)。
- 11 个阶段:像是 A 区内的流水线(卸货 → 扫描 → 打包 → 装车…)。
- my_module:像是你自定义的一个打包机器人(安装在“打包”阶段)。
无论分拣规则如何,流水线的阶段顺序不变,你的机器人只在自己注册的阶段工作! 必须先匹配到 location,然后才会按照固定的 11 个阶段顺序 执行相关模块的逻辑。
6. 总结
1. NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE
- 作用:HTTP 请求头读取完成后,进入框架。
- 可挂载:✅ 可以。
- 典型模块:
realip_module(替换客户端 IP)。 - 开发者实践:常用于 预处理(黑名单、限速、header 修改)。
2. NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE
- 作用:确定虚拟主机之前的 rewrite 阶段。
- 可挂载:✅ 可以。
- 典型模块:
rewrite_module(基于 server 的 rewrite)。 - 开发者实践:用于 域名级别跳转 或 请求预处理。
3. NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE
- 作用:匹配
location配置。 - 可挂载:❌ 不可以。
- 典型模块:无(核心逻辑)。
- 开发者实践:这是 Nginx 内部阶段,不能扩展。
4. NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE
- 作用:进入 location 之后的 rewrite 阶段。
- 可挂载:✅ 可以。
- 典型模块:
rewrite_module(基于 location 的 rewrite)。 - 开发者实践:常用于 URI 改写、跳转。
5. NGX_HTTP_POST_REWRITE_PHASE
- 作用:rewrite 后收尾,可能重新跳回 FIND_CONFIG。
- 可挂载:❌ 不可以。
- 典型模块:无(核心逻辑)。
- 开发者实践:框架内部 防死循环 控制。
6. NGX_HTTP_PREACCESS_PHASE
- 作用:访问控制前的准备工作。
- 可挂载:✅ 可以。
- 典型模块:
limit_req_module(请求速率限制)。 - 开发者实践:可做 WAF 检查、频率控制。
7. NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE
- 作用:权限检查。
- 可挂载:✅ 可以。
- 典型模块:
access_module(allow/deny)。 - 开发者实践:做 IP 白名单、认证 等。
8. NGX_HTTP_POST_ACCESS_PHASE
- 作用:收尾,判断 access 的结果。
- 可挂载:❌ 不可以。
- 典型模块:无(框架逻辑)。
- 开发者实践:框架自动 拦截拒绝,无需扩展。
9. NGX_HTTP_TRY_FILES_PHASE
- 作用:处理
try_files指令。 - 可挂载:❌ 一般不可以(专属
try_files模块)。 - 典型模块:
try_files。 - 开发者实践:属于 特殊保留阶段。
10. 🔴 NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE
- 作用:生成 HTTP 响应的核心阶段。
- 可挂载:✅ 可以(最重要)。
- 典型模块:
static_module(静态文件)proxy_module(反向代理)fastcgi_module
- 两种介入方式:
- 独占式(clcf->handler)
- 在
location里直接绑定一个 handler。 - 一旦设置,只会执行该 handler,不会再遍历其他 content handlers。
- 用于 静态服务、代理、业务 API。
- 在
- 链式(phase handler 队列)
- 如果
clcf->handler没有设置,则遍历cmcf->phases[CONTENT_PHASE].handlers。 - 多个 handler 可以依次尝试,返回
NGX_DECLINED则继续下一个。 - 最终仍然只有 第一个成功处理的 handler 会生成响应。
- 如果
- 独占式(clcf->handler)
- 开发者实践:
- 独占式:适合业务响应模块。
- 链式:适合“候补型”模块,例如尝试处理部分请求。
11. NGX_HTTP_LOG_PHASE
- 作用:请求完成后,写日志。
- 可挂载:✅ 可以。
- 典型模块:
log_module。 - 开发者实践:用于 访问日志、统计、监控。
总结表格
| 阶段 | 功能 | 可否挂载 | 模块示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POST_READ | 请求头读完 | ✅ | realip | 预处理 |
| SERVER_REWRITE | server 级 rewrite | ✅ | rewrite | 域名跳转 |
| FIND_CONFIG | 匹配 location | ❌ | - | 内部逻辑 |
| REWRITE | location 级 rewrite | ✅ | rewrite | URL 改写 |
| POST_REWRITE | rewrite 收尾 | ❌ | - | 防死循环 |
| PREACCESS | 访问前准备 | ✅ | limit_req | WAF、限流 |
| ACCESS | 权限检查 | ✅ | access | allow/deny |
| POST_ACCESS | access 收尾 | ❌ | - | 内部逻辑 |
| TRY_FILES | try_files 处理 | ❌ | try_files | 专属模块 |
| 🔴 CONTENT | 生成响应 | ✅ | static/proxy/fastcgi | 独占式 / 链式 |
| LOG | 写日志 | ✅ | log | 日志统计 |
checker 方法对应
进入某个阶段 → 执行该阶段的 checker 方法 → checker 内部依次调用该阶段注册的 handler
| Checker 方法 | 对应的 Phase | 用途 / 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| ngx_http_core_generic_phase | POST_READ、PREACCESS、POST_ACCESS、LOG | 通用 checker,逐个调用 handler;适合限流、统计、日志等模块 |
| ngx_http_core_rewrite_phase | SERVER_REWRITE、REWRITE | URI 重写;如果 URI 改变,跳回 FIND_CONFIG 重新匹配 |
| ngx_http_core_find_config_phase | FIND_CONFIG | 查找匹配的 server/location 配置;决定请求落点 |
| ngx_http_core_post_rewrite_phase | POST_REWRITE | rewrite 收尾;确认是否需要二次 FIND_CONFIG |
| ngx_http_core_access_phase | ACCESS | 权限认证、allow/deny;任一拒绝即终止请求 |
| ngx_http_core_try_files_phase | TRY_FILES | 处理 try_files;命中直接返回,未命中进入 CONTENT |
| ngx_http_core_content_phase | CONTENT | 执行内容生成 handler(static、proxy、fastcgi…),产出响应 |
Nginx Phase 与 Checker、Handler 理解
核心概念区分
| 名称 | 定义 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| Phase(阶段) | Nginx 请求处理生命周期中的一个逻辑步骤,如 rewrite、access、content 等 | 作为状态机的“节点”,用来组织请求处理流程 |
| Checker 方法 | 针对某一类阶段的调度函数,如 ngx_http_core_generic_phase、ngx_http_core_rewrite_phase | 调度并执行属于该 checker 管辖的阶段的所有 handler,决定流程是否继续 |
| Handler 方法 | 模块注册在某个阶段的实际回调函数,如 ngx_http_rewrite_handler | 执行具体功能(rewrite URI、权限控制、生成内容等) |
注意:一个 checker 方法可能管理多个阶段,所以并不是一一对应。
调用流程(准确版)
- 请求到达 Nginx 核心 HTTP 框架
- 状态机选择当前阶段(phase)
- 根据当前阶段找到对应的 checker
- 例如:rewrite 阶段 →
ngx_http_core_rewrite_phase - access 阶段 →
ngx_http_core_access_phase - LOG、POST_ACCESS 等阶段 →
ngx_http_core_generic_phase
- 例如:rewrite 阶段 →
- Checker 内部
- 遍历该阶段注册的 handler 列表
- 按顺序调用 handler
- 根据 handler 返回值决定:继续下一个 handler、跳到下一阶段或挂起等待事件
- 处理完成
- 状态机推进到下一个阶段
- 重复上述过程直到请求完成
