1. ngx_command_t
1.1 示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_mytest_commands[] =
{
{
ngx_string("test_flag"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF | NGX_CONF_FLAG,
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest_conf_t, my_flag),
NULL
},
}
typedef struct ngx_command_s ngx_command_t;
struct ngx_command_s {
ngx_str_t name; // 指令名称,如 "listen"、"server_name" 等
ngx_uint_t type; // 指令的类型和上下文,如 NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF、NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF , 简单来说就是可以出现在哪些配置体中。
char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf); // 指令的解析函数
ngx_uint_t conf; // 指令的配置存储位置,如 NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF_OFFSET、NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF_OFFSET, 简单来说就是这个配置存放于ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 的哪个块中, server local?
ngx_uint_t offset; // 指令在配置结构体中的偏移量,用于定位存储位置
void *post; // 指令解析后的回调函数,通常为 NULL
};
1.2 ngx_uint_t type;
| 类型 | 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 指令类型 | NGX_CONF_NOARGS | 指令不接受任何参数。 |
NGX_CONF_TAKE1 | 指令接受 1 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE2 | 指令接受 2 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE3 | 指令接受 3 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE4 | 指令接受 4 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE5 | 指令接受 5 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE6 | 指令接受 6 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE7 | 指令接受 7 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE12 | 指令接受 1 或 2 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE13 | 指令接受 1 或 3 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE23 | 指令接受 2 或 3 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE123 | 指令接受 1、2 或 3 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_TAKE1234 | 指令接受 1、2、3 或 4 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_FLAG | 指令是一个标志,接受 on 或 off 作为参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_1MORE | 指令至少接受 1 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_2MORE | 指令至少接受 2 个参数。 | |
NGX_CONF_MULTI | 指令可以接受多个参数(数量不限)。 | |
| 指令上下文 | NGX_MAIN_CONF | 指令可以出现在全局配置块中(main 级别)。 |
NGX_EVENT_CONF | 指令可以出现在 events{} 块中。 | |
NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF | 指令可以出现在 http{} 块中。 | |
NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF | 指令可以出现在 server{} 块中。 | |
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF | 指令可以出现在 location{} 块中。 | |
NGX_HTTP_UPS_CONF | 指令可以出现在 upstream{} 块中。 | |
NGX_HTTP_SIF_CONF | 指令可以出现在 server{} 块中的 if 条件中。 | |
NGX_HTTP_LIF_CONF | 指令可以出现在 location{} 块中的 if 条件中。 | |
NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF | 指令可以出现在 limit_except{} 块中。 | |
NGX_STREAM_MAIN_CONF | 指令可以出现在 stream{} 块中。 | |
NGX_STREAM_SRV_CONF | 指令可以出现在 server{} 块中(stream 模块)。 | |
NGX_MAIL_MAIN_CONF | 指令可以出现在 mail{} 块中。 | |
NGX_MAIL_SRV_CONF | 指令可以出现在 server{} 块中(mail 模块)。 | |
| 其他标志 | NGX_CONF_BLOCK | 指令是一个块指令(如 server{}、location{})。 |
NGX_CONF_ANY | 指令可以出现在任何配置块中。 | |
NGX_CONF_UNSET | 指令的值可以被取消设置(如 unset)。 |
1.3 char (set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
1
nginx 提供14 中预设方法来解析配置
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot | 解析 on 或 off 标志,并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_str_slot | 解析字符串参数,并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_str_array_slot | 解析字符串数组参数,并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_keyval_slot | 解析键值对参数,并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_num_slot | 解析数字参数,并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_size_slot | 解析大小参数(如 10k、20m),并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_off_slot | 解析偏移量参数(如 10k、20m),并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_msec_slot | 解析时间参数(如 10ms、20s),并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_sec_slot | 解析时间参数(以秒为单位),并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_bufs_slot | 解析缓冲区数量和大小的参数,并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_enum_slot | 解析枚举值参数,并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_bitmask_slot | 解析位掩码参数,并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_access_slot | 解析访问权限参数(如 0644),并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
ngx_conf_set_path_slot | 解析路径参数(如 /path/to/file),并将结果存储到配置结构体中。 |
挑出一个例子,ngx_conf_set_flag_slot 说明:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
char *
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
char *p = conf;
ngx_str_t *value;
ngx_flag_t *fp;
ngx_conf_post_t *post;
fp = (ngx_flag_t *) (p + cmd->offset);
if (*fp != NGX_CONF_UNSET) {
return "is duplicate";
}
value = cf->args->elts;
if (ngx_strcasecmp(value[1].data, (u_char *) "on") == 0) {
*fp = 1;
} else if (ngx_strcasecmp(value[1].data, (u_char *) "off") == 0) {
*fp = 0;
} else {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"invalid value \"%s\" in \"%s\" directive, "
"it must be \"on\" or \"off\"",
value[1].data, cmd->name.data);
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
if (cmd->post) {
post = cmd->post;
return post->post_handler(cf, post, fp);
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
几点说明:
1. 参数conf就是http框架传给我们的,在ngx_http_mytest_create_loc_conf 回调方法中分配的结构体ngx_http_mytest_conf_t
2. cf->args是1个ngx_array_t队列,它的成员都是ngx_str_t结构。我们用value指向ngx_array_t的elts内容,其中value[1]就是第1个参数,同理value[2]是第2个参数
3. ngx_command_t *cmd 则是触发命令 ~
1.4 ngx_uint_t conf;
| 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF_OFFSET | 配置存储在 main 级别的配置结构体中(对应 http{} 块)。 |
NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF_OFFSET | 配置存储在 server 级别的配置结构体中(对应 server{} 块)。 |
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET | 配置存储在 location 级别的配置结构体中(对应 location{} 块)。 |
NGX_STREAM_MAIN_CONF_OFFSET | 配置存储在 stream 模块的 main 级别配置结构体中(对应 stream{} 块)。 |
NGX_STREAM_SRV_CONF_OFFSET | 配置存储在 stream 模块的 server 级别配置结构体中(对应 server{} 块)。 |
NGX_MAIL_MAIN_CONF_OFFSET | 配置存储在 mail 模块的 main 级别配置结构体中(对应 mail{} 块)。 |
NGX_MAIL_SRV_CONF_OFFSET | 配置存储在 mail 模块的 server 级别配置结构体中(对应 server{} 块)。 |
1.5 ngx_uint_t offset
Nginx 首先通过 conf 成员找到应该用哪个结构体来存放,然后通过 offset 成员找到这个结构体中的相应成员,以便存放该配置。如果是自定义的专用配置项解析方法(只解析某一个配置项),则可以不设置 offset 的值。
1.6 NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF 与 NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET 字段
- main 配置块的数据存储在 ngx_http_core_main_conf_t 结构体中。
- server 配置块的数据存储在 ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t 结构体中。
- location 配置块的数据存储在 ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t 结构体中。
2. Nginx 配置问题
2.1 ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 结构体
ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 是一个关键的结构体,用于管理 HTTP 模块的配置数据。它的定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
typedef struct {
void **main_conf; // 指向所有模块的全局配置数组
void **srv_conf; // 指向所有模块的 server 配置数组
void **loc_conf; // 指向所有模块的 location 配置数组
} ngx_http_conf_ctx_t;
在 Nginx 解析配置文件时,会按照以下流程存储配置数据:
- 调用每个模块的 create_main_conf、create_srv_conf 和 create_loc_conf 方法,生成配置结构体。
- 将配置结构体的指针分别存储到 main_conf、srv_conf 和 loc_conf 数组中。
- 将这三个数组的指针保存到 ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 结构体中。
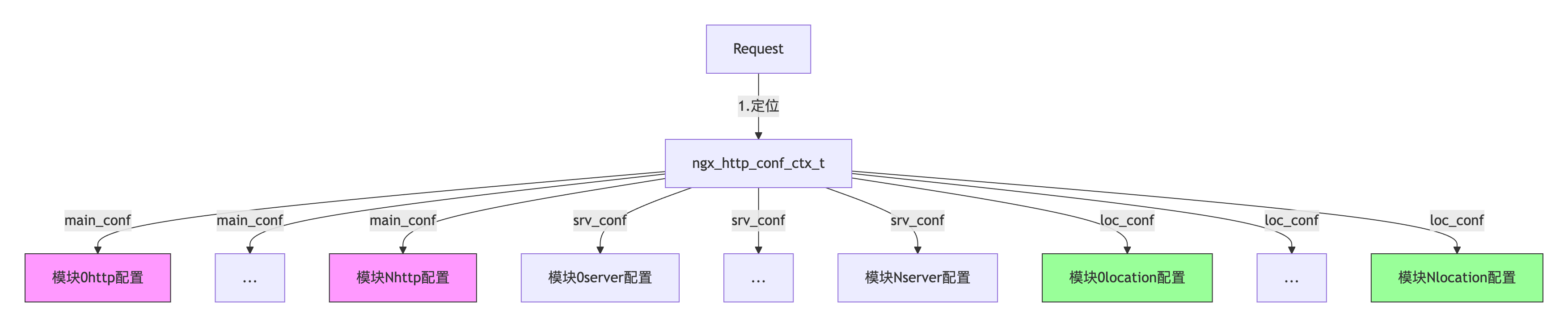
2.2 create xxx configuration
在 Nginx 的 HTTP 模块开发中,create server configuration 是一个可选的回调函数,用于为每个 server 块创建配置结构体, 划重点, 结构体。
如果不定义, 默认结构体如下:
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t:用于存储 location{} 块的配置。 - ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t:用于存储 server{} 块的配置。 - ngx_http_core_main_conf_t:用于存储 http{} 块的配置。
默认结构体
当模块 不定义 create_server_conf 时,Nginx 核心会自动使用以下内置结构体,默认结构体:核心模块已提供基础字段,适用于简单需求.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// http{} 块配置(必须通过 create_main_conf 自定义)
typedef struct {
ngx_array_t servers; // 所有server{}配置的集合
ngx_http_phase_engine_t phase_engine; // HTTP处理阶段引擎
ngx_uint_t *server_names_hash_max_size;
/* 其他30+个全局HTTP配置字段... */
} ngx_http_core_main_conf_t;
// server{} 块配置(默认结构体)
struct ngx_http_core_srv_conf_s {
ngx_str_t server_name; // 服务器名
ngx_array_t listen; // 监听端口
/* 其他40+个核心字段... */
};
// location{} 块配置(默认结构体)
struct ngx_http_core_loc_conf_s {
ngx_str_t name; // location匹配规则
void **handler; // 内容处理器
/* 其他30+个核心字段... */
};
默认结构体 与 自定义结构体是否可以通用 默认结构体(如 ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t)和 自定义结构体 完全可以协同工作
创建过程 默认结构体:由 ngx_http_core_module 强制创建(索引0) 自定义结构体:由模块通过 create_loc_conf 创建(索引n)
两个api
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mymodule_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) { // 同时使用两种配置 ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); ngx_http_mymodule_loc_conf_t *mlcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_mymodule); // 示例:当模块启用且location非内部时处理 if (mlcf->enable && !clcf->internal) { ngx_log_debug2(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_HTTP, r->connection->log, 0, "core: %d, my: %V", clcf->internal, &mlcf->custom_header); } }
一些易混淆的api: ngx_http_conf_get_xxx
1. 区别概览:
| 宏 | 返回值类型 | 数据来源 | 使用阶段 | 典型场景 | 关键区别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf | 模块自定义的 loc_conf 结构体 | 配置上下文 cf->ctx | 配置解析阶段 | 解析nginx.conf指令时 | 获取原始配置(未合并),用于模块指令回调和配置合并函数 |
ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf | 模块自定义的 loc_conf 结构体 | 请求对象 r->loc_conf | 请求处理阶段 | 处理HTTP请求的业务逻辑中 | 获取最终生效配置(已合并继承),只能用于请求处理相关的回调函数 |
2. api:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// 在请求处理阶段获取配置
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mymodule_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) {
ngx_http_mymodule_loc_conf_t *mlcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_mymodule_module);
// 使用 mlcf->custom_setting 等字段
}
// 在配置解析阶段获取配置
static char *ngx_http_mymodule_directive(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) {
ngx_http_mymodule_loc_conf_t *mlcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_mymodule_module);
// 设置 mlcf->custom_setting 等字段
}
3.举例说明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
/* 请求处理函数 */
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mymodule_content_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
// 使用 ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf 获取运行时配置
ngx_http_mymodule_loc_conf_t *mlcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_mymodule_module);
if (!mlcf->enable) {
return NGX_DECLINED;
}
// 设置响应头
r->headers_out.content_type.len = sizeof("text/plain") - 1;
r->headers_out.content_type.data = (u_char *) "text/plain";
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
// 发送响应体
ngx_buf_t *b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
ngx_chain_t out;
out.buf = b;
out.next = NULL;
b->pos = mlcf->response_text.data;
b->last = mlcf->response_text.data + mlcf->response_text.len;
b->memory = 1;
b->last_buf = 1;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = mlcf->response_text.len;
ngx_http_send_header(r);
return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);
}
/* 注册内容处理阶段 */
// 指令定义
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_hello_commands[] = {
{
ngx_string("hello_message"), // 指令名
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF | NGX_CONF_TAKE1, // 使用位置和参数限制
ngx_http_hello_set_message, // 解析指令的函数
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET, // 配置存储在结构中的偏移量
0, // 用于指令的标志,通常为 0
NULL // 指令的回调,通常为 NULL
},
ngx_null_command
};
// 配置指令解析函数
static char *ngx_http_hello_set_message(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) {
ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t *hlcf = conf;
ngx_str_t *value = cf->args->elts;
hlcf->message = value[1];
// 设置 handler
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
clcf->handler = ngx_http_hello_handler; // 注册处理函数
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
4. ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf 是不是可以又用官方配置 又用自定义配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// 打开抽屉,找到标着"核心模块"的格子
// 这个格子里的东西是 Nginx 官方定义的(如 alias、proxy_pass 等指令的配置)
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf =
ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module);
// 同一个抽屉里,找到标着"我的模块"的格子
// 这个格子里的东西是您自己定义的(如 my_custom_header 等指令的配置)
ngx_http_mymodule_loc_conf_t *mlcf =
ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_mymodule_module);
5. ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf 是不是可以又用官方配置 又用自定义配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf =
ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
// 可访问 clcf->alias, clcf->proxy_pass 等核心字段
ngx_http_mymodule_loc_conf_t *mlcf =
ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_mymodule_module);
// 可访问 mlcf->custom_setting 等自定义字段
5. 指令解析函数参数解析
1
static char *ngx_http_hello_set_message(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
| 参数 | 类型 | 作用 | 典型用法示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
cf | ngx_conf_t* | 配置解析上下文,包含当前解析状态的所有信息 | 访问 cf->args 获取指令参数,cf->pool 分配内存 |
cmd | ngx_command_t* | 当前指令的定义,描述指令的类型和约束 | 检查 cmd->type 确认指令类型,cmd->name 获取指令名 |
conf | void* | 模块的配置存储位置 | 强制转换为模块自定义的配置类型(如 ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t*)并修改字段 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// 一个例子说清楚
static char *ngx_http_hello_set_message(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) {
// 1. 获取模块配置结构体
ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t *hlcf = (ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t *)conf;
// 2. 从cf获取指令参数(如 hello_message "Hi")
ngx_str_t *args = cf->args->elts;
hlcf->message = args[1]; // args[0]是指令名,args[1]是第一个参数
// 3. 通过cmd检查指令类型
if (!(cmd->type & NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF)) {
return "directive only allowed in location context";
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
6. 若创建多个结构体, ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf 返回的是哪一个?
每个模块(包括自定义模块)只能有一个主配置结构体 ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf 永远返回该模块在 create_loc_conf 中创建的结构体。
2.3 配置解析流程简述
引用三张图吧, 比较清晰


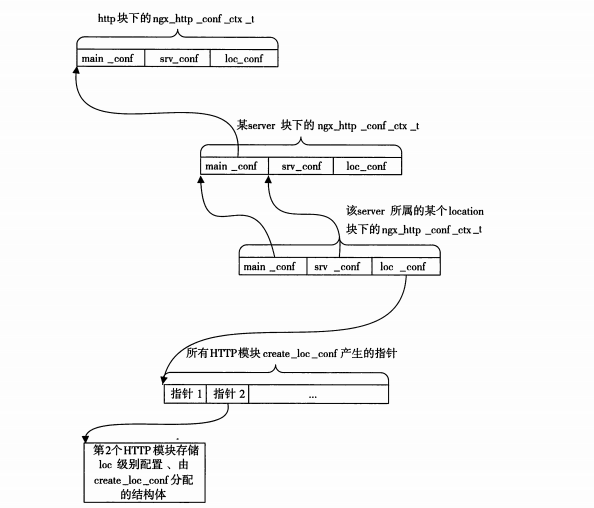
2.4 有关配置合并的问题解析
如果实现了create_main_conf方法,那么它所创建的结构体只会存放直接出现在http{}块下的配置项,因此create_main_conf只会被调用一次。 如果实现了create_srv_conf方法,那么它所创建的结构体既会存放直接出现在http{}块下的配置项,也会存放直接出现在server{}块下的配置项。为什么呢?这其实是HTTP框架的一种优秀设计。例如,虽然某个配置项是针对于server虚拟主机才生效的,但http{}块下面可能有多个server{}块,对于用户来说,如果希望在http{}块下面写入这个配置项后对所有的server{}块都生效,这应当是允许的,因为它减少了用户的工作量。而对于HTTP框架来说,它会先调用create_srv_conf方法为http{}块创建配置结构体,再为每个server{}块调用create_srv_conf方法创建配置结构体
举例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
typedef struct {
ngx_str_t my_config; // 配置项
} ngx_http_mytest_srv_conf_t;
static void *
ngx_http_mytest_create_srv_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
ngx_http_mytest_srv_conf_t *conf;
conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_mytest_srv_conf_t));
if (conf == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// 初始化配置
conf->my_config.len = 0;
conf->my_config.data = NULL;
return conf;
}
static char *
ngx_http_mytest_merge_srv_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child)
{
ngx_http_mytest_srv_conf_t *prev = parent; // 父配置(http{} 块)
ngx_http_mytest_srv_conf_t *conf = child; // 子配置(server{} 块)
// 如果子配置未设置,则使用父配置
if (conf->my_config.len == 0) {
conf->my_config = prev->my_config;
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_mytest_commands[] = {
{
ngx_string("my_config"), // 指令名称
NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF | NGX_CONF_TAKE1, // 支持 http{} 和 server{} 块
ngx_conf_set_str_slot,
NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF_OFFSET, // 配置数据存储到 server 配置块
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest_srv_conf_t, my_config), // 存储到 my_config 字段
NULL
},
ngx_null_command
};
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_mytest_module_ctx = {
NULL, // preconfiguration
NULL, // postconfiguration
NULL, // create main configuration (移除)
NULL, // init main configuration
ngx_http_mytest_create_srv_conf, // create server configuration
ngx_http_mytest_merge_srv_conf, // merge server configuration
NULL, // create location configuration
NULL // merge location configuration
};
ngx_module_t ngx_http_mytest_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_mytest_module_ctx, // module context
ngx_http_mytest_commands, // module directives
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, // module type
NULL, // init master
NULL, // init module
NULL, // init process
NULL, // init thread
NULL, // exit thread
NULL, // exit process
NULL, // exit master
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
http {
my_config "global_value"; # 在 http{} 块中写配置
server {
# 未设置局部配置,使用全局配置
}
server {
my_config "server2_value"; # 在 server{} 块中写配置
}
}
- 对于第一个 server{} 块,my_config 的值是 “global_value”(来自 http{} 块)。
- 对于第二个 server{} 块,my_config 的值是 “server2_value”(来自 server{} 块)。
2.5 问题答疑
NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF NGX_CONF_TAKE1, // 只支持 server 块 ; 还可以在http 块中写配置吗? 即使指令标志中只写了 NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF,仍然可以在 http{} 块中写配置。这是因为 create_srv_conf 方法的设计允许配置项在 http{} 块和 server{} 块中都生效。
什么要在 解析http 配置阶段调用 ngx_http_mytest_create_srv_conf 函数?
Nginx 的配置解析是按照 块(block) 的层级进行的。在解析 http{} 块时,Nginx 会:- 调用 create_main_conf 方法,为 http{} 块创建全局配置结构体。
- 调用 create_srv_conf 方法,为 http{} 块创建 server 配置结构体。
- 在解析 server{} 块时,再次调用 create_srv_conf 方法,为每个 server{} 块创建独立的 server 配置结构体。
为什么在 http{} 块中调用 create_srv_conf?- 在 http{} 块中调用 create_srv_conf 方法的主要原因是:支持全局默认配置。
3. 模块上下文
总结来说: 每一个模块 对应 每一个 请求 , 都有一个单独的上下文。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
typedef struct
{
ngx_http_status_t status;
ngx_str_t backendServer;
} ngx_http_mytest_ctx_t;
//首先建立http上下文结构体ngx_http_mytest_ctx_t
ngx_http_mytest_ctx_t* myctx = ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, ngx_http_mytest_module);
if (myctx == NULL)
{
myctx = ngx_palloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_mytest_ctx_t));
if (myctx == NULL)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
//将新建的上下文与请求关联起来
ngx_http_set_ctx(r, myctx, ngx_http_mytest_module);
}
4. 解惑说明
1
Nginx 配置解析中 `create_conf` 和 `指令处理函数` 的区别
这是一个常被混淆的点。你说的:
- 创建配置结构体的函数(比如
create_loc_conf) - 处理配置指令的函数(比如
ngx_http_mytest)
它们作用不同、触发时机不同、目的也不同。
✅ 一、create_loc_conf —— 创建配置结构体内存
这个函数在解析配置文件之前,Nginx 主框架就会调用每个模块的这个函数,用于:
- 为该模块在对应配置层级(main/srv/loc)下分配一块内存空间。
- 返回的指针会被保存在模块上下文中,后续解析指令、合并配置时都用它。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
static void *
ngx_http_mytest_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf) {
ngx_http_mytest_conf_t *conf;
conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_mytest_conf_t));
conf->my_flag = NGX_CONF_UNSET; // 设置默认值(unset)
return conf;
}
✔️ 它是为 “这个 location 的模块配置” 分配结构体空间的。
✅ 二、ngx_http_mytest() —— 解析指令的处理函数
这个是和 ngx_command_t 绑定的,当配置文件中出现了对应的指令(比如 my_flag on;)时:
- 配置解析器会查找这个指令
- 找到你模块定义的
ngx_http_mytest函数 - 调用它来解析参数并写入对应的配置结构体
例如:
1
2
3
location / {
my_flag on;
}
指令定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_mytest_commands[] = {
{
ngx_string("my_flag"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_FLAG,
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest_conf_t, my_flag),
NULL
},
ngx_null_command
};
✔️ 它是对配置文件中每一条出现的指令进行处理。
🔁 关系总结表
| 类型 | 函数 | 被谁调用 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 创建配置结构体 | create_loc_conf | Nginx 在解析开始时 | 为模块在某个层级准备配置内存 |
| 合并配置结构体 | merge_loc_conf | 配置解析完成时 | 把父层级配置合并到子层级 |
| 配置指令解析函数 | ngx_http_mytest(或绑定的 set_xxx_slot) | 解析到 my_flag 这类指令时 | 把指令的参数写入配置结构体 |
🌟 实际流程举例
- 配置文件开始解析 location 块,框架会调用你模块的
create_loc_conf,返回mytest_conf指针; - 配置中出现
my_flag on;,框架根据ngx_command_t找到你的ngx_http_mytest函数; - 函数读取
"on",转换成1,写入mytest_conf->my_flag = 1;; - 后续如果还有更细的 location,父配置会和子配置合并,调用
merge_loc_conf。
如果你需要将图示逐步对应上函数的调用时机,也可以在图中标注继续讲解。
