1. 概览
1. nginx 模块分类
// 25.8.14 补充
《深入理解nginx》书中, Nginx源码中明确标记为NGX_CORE_MODULE类型的模块只有以下6个,它们是Nginx运行的最底层基础:
Nginx的核心模块采用分层架构设计,每个核心模块不仅是功能实现者,更是模块类型的管理者。ngx_events_module、ngx_http_module和ngx_mail_module这三个核心模块分别定义了NGX_EVENT_MODULE、NGX_HTTP_MODULE和NGX_MAIL_MODULE三种模块类型,并全权管理对应类型的模块。这种设计赋予核心模块双重角色:既作为基础功能的提供者,又作为模块体系的架构师,通过类型定义实现功能解耦,使得事件处理、HTTP服务和邮件代理等不同领域的模块能够独立演化,同时保持整体架构的统一性。
| 模块名称 | 源码文件 | 核心作用 |
|---|---|---|
ngx_core_module | ngx_core.c | 解析main配置块(worker_processes/pid等) |
ngx_errlog_module | ngx_errlog.c | 错误日志系统初始化 |
ngx_events_module | ngx_event.c | 事件驱动框架抽象层 |
ngx_openssl_module | ngx_event_openssl.c | OpenSSL加密库集成 |
ngx_http_module | ngx_http.c | HTTP协议框架 |
ngx_mail_module | ngx_mail.c | 邮件协议框架 |
| 大类模块 | 作用 | 配置块 | 示例模块 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core 模块 | Nginx 基础功能(进程、事件、日志等) | 全局或 events {} | ngx_core_modulengx_events_module |
| HTTP 模块 | 处理 HTTP/HTTPS 请求(Web 服务) | http {} | ngx_http_core_module |
| Mail 模块 | 代理邮件协议(SMTP/IMAP/POP3) | mail {} | ngx_mail_core_module |
| Stream 模块 | 处理 TCP/UDP 流量(四层代理) | stream {} | ngx_stream_core_module |
2. http 模块分类
HTTP 模块是 Nginx 中处理 HTTP/HTTPS 请求的核心模块,负责请求解析、路由、过滤、反向代理等。以下是 HTTP 模块的详细分类和核心机制:
2.1 按照4 层架构分类
举例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
http {
# 1. 核心结构
server {
listen 80;
# 2. 请求处理(三选一)
location /static {
root /data; # 静态资源
}
location /api {
proxy_pass http://backend; # 反向代理
}
# 3. 响应加工(可叠加)
gzip on; # 压缩
sub_filter 'old' 'new'; # 内容替换
# 4. 辅助控制
deny 192.168.1.1; # 访问控制
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log; # 日志
}
# 负载均衡定义
upstream backend {
server 10.0.0.1:8080;
}
}
1. 核心结构模块
- 作用:定义 HTTP 基础框架,不可禁用。
- 模块:
ngx_http_core_module - 关键指令:
1 2
server { listen 80; } location / { ... }
2. 请求处理模块
- 作用:直接生成响应或转发请求(必须选择一种,互斥)。
- 子类与示例:
| 类型 | 功能 | 模块 | 指令 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 静态资源 | 返回文件/目录 | ngx_http_static_module | root, try_files |
| 反向代理 | 转发请求到后端 | ngx_http_proxy_module | proxy_pass |
| FastCGI | 处理 PHP/Python 等动态请求 | ngx_http_fastcgi_module | fastcgi_pass |
| 重定向 | 返回 3xx 跳转 | ngx_http_rewrite_module | return 302, rewrite |
3. 响应加工模块
- 作用:对已有响应进行修改(可叠加使用)。
- 子类与示例:
| 类型 | 功能 | 模块 | 指令 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩 | Gzip/Brotli 压缩 | ngx_http_gzip_module | gzip on |
| 内容替换 | 修改响应文本 | ngx_http_sub_filter_module | sub_filter |
| 缓存控制 | 设置缓存头 | ngx_http_headers_module | expires, add_header |
4. 辅助控制模块
- 作用:安全、日志、负载均衡等。
- 子类与示例:
| 类型 | 功能 | 模块 | 指令 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 访问控制 | IP/密码限制 | ngx_http_access_module | allow, deny |
| 负载均衡 | 多后端服务器分发 | ngx_http_upstream_module | upstream |
| 日志记录 | 记录请求信息 | ngx_http_log_module | access_log |
5. 总结
1. 层级关系: 核心结构 → 选择处理方式 → 加工响应 → 附加控制。 2. 互斥性: 每个请求只能由 一个请求处理模块 响应(如不能同时用 proxy_pass 和 static)。
- 叠加性: 响应加工模块 可组合使用(如 Gzip + 内容替换)。
2.2 按照是否为过滤模块分类
HTTP 模块可进一步细分为非过滤模块和过滤模块,具体如下:
| 模块类型 | 功能 | 典型模块示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 非过滤模块 | 处理请求逻辑(路由、代理等) | ngx_http_core_module、ngx_http_proxy_module |
| Header Filters | 修改 HTTP 响应头 | ngx_http_headers_filter_module |
| Body Filters | 修改 HTTP 响应体 | ngx_http_gzip_filter_module |
2.3 总结
过滤模块的执行确实 不依赖阶段(Phase),而是通过 全局过滤链 动态执行。要准确判断一个自定义模块是否为过滤模块,需要从 代码实现机制 和 运行时行为 两个维度验证。
1. 过滤模块的绝对判定标准(代码级)
(1) 必须插入全局过滤链
1
2
3
4
5
6
// 在模块初始化函数中
ngx_http_next_header_filter = ngx_http_top_header_filter;
ngx_http_top_header_filter = my_header_filter; // 插入Header过滤链
ngx_http_next_body_filter = ngx_http_top_body_filter;
ngx_http_top_body_filter = my_body_filter; // 插入Body过滤链
如果没有这段代码,100%不是过滤模块
(2) 必须实现过滤函数签名
1
2
3
4
5
// Header过滤函数
static ngx_int_t my_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r);
// Body过滤函数
static ngx_int_t my_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in);
(3) 必须调用下一跳过滤函数
1
2
3
4
static ngx_int_t my_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in) {
// 处理逻辑...
return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in); // 关键!
}
2. 过滤模块的运行时特征
(1) 依赖前置响应
1
2
3
4
location / {
my_filter "text"; # 过滤模块
proxy_pass http://backend; # 需要前置生成器
}
(2) 可叠加执行
1
2
3
4
5
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
my_filter "A"; # 过滤模块A
other_filter "B"; # 过滤模块B → 可叠加
}
3. 快速验证方案
步骤1:检查模块初始化函数
1
2
3
// 过滤模块必有:
// Nginx的全局header过滤链入口指针,所有header过滤模块通过此链串联。
ngx_http_top_header_filter = my_header_filter;
步骤2:测试配置依赖
1
2
3
location / {
my_custom_module on; # 单独使用
}
- 报错要求前置响应 → 过滤模块
- 能独立工作 → 非过滤模块
总结对比表
| 特征 | 过滤模块 | 非过滤模块 | |——————–|—————————-|————————–| | 注册方式 | 插入ngx_http_top_*_filter | 注册ngx_http_handler_pt | | 执行时机 | 所有响应生成后 | 特定阶段 | | 返回值 | 必须调用next_filter | 直接返回状态码 | | 配置依赖 | 需要前置响应 | 可独立运行 |
2. HTTP 请求处理的 11 个阶段
Nginx 将 HTTP 请求处理分为 11 个阶段,非过滤模块可以挂载到不同阶段执行逻辑:
| 阶段 | 说明 | 典型模块 |
|---|---|---|
| NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE | 读取请求头后立即执行 | ngx_http_realip_module(修改客户端IP) |
| NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE | Server 块内的 URL 重写 | ngx_http_rewrite_module |
| NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE | 查找匹配的 Location 配置 | (Nginx 内部逻辑,无模块直接介入) |
| NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE | Location 块内的 URL 重写 | ngx_http_rewrite_module |
| NGX_HTTP_POST_REWRITE_PHASE | 重写后的后处理 | (通常无模块介入) |
| NGX_HTTP_PREACCESS_PHASE | 访问控制前的预处理 | ngx_http_limit_req_module(限流) |
| NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE | 访问权限控制(如 IP 黑白名单) | ngx_http_access_module |
| NGX_HTTP_POST_ACCESS_PHASE | 访问控制后的处理 | (通常无模块介入) |
| NGX_HTTP_PRECONTENT_PHASE | 生成内容前的预处理 | ngx_http_try_files_module(检查文件是否存在) |
| NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE | 生成响应内容(核心阶段) | ngx_http_proxy_module(反向代理) |
| NGX_HTTP_LOG_PHASE | 请求日志记录 | ngx_http_log_module |
3. 过滤模块的执行顺序
过滤模块(Header/Body Filters)不依赖阶段,而是通过过滤链执行:
| 过滤模块类型 | 执行顺序 | 典型模块 |
|---|---|---|
| Header Filters | 按 ngx_modules[] 顺序执行 | ngx_http_headers_filter_module |
| Body Filters | 反向 ngx_modules[] 顺序执行 | ngx_http_gzip_filter_module |
为什么 Body Filters 要反向执行?
假设有两个 Body Filters:
- 分块模块(A):将响应体分块传输。
- 压缩模块(B):压缩响应体。
逻辑需求: 应该先压缩整个响应体,再分块传输(即 B → A)。 但 Nginx 的模块是按 A → B 顺序编译的,因此通过反向执行实现 B → A 的实际效果。
4. HTTP 模块开发关键点
(1) 非过滤模块如何挂载到阶段?
在模块的 postconfiguration 回调中注册阶段处理器:
1
2
3
4
5
static ngx_int_t my_postconfiguration(ngx_conf_t *cf) {
ngx_http_handler_pt *h = ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE].handlers);
*h = my_content_handler; // 模块的处理函数
return NGX_OK;
}
(2) 过滤模块如何注册?
通过 ngx_http_next_header_filter 或 ngx_http_next_body_filter 插入过滤链
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
static ngx_int_t my_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r) {
// 修改响应头
return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
}
static ngx_int_t my_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in) {
// 修改响应体
return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in);
}
5. 总结
- HTTP 模块的核心机制 - 非过滤模块:按 11 个阶段顺序执行(如代理、重定向)。 - Header Filters:按模块编译顺序处理响应头。 - Body Filters:反向模块编译顺序处理响应体(确保逻辑正确性)。
1. Nginx HTTP 模块详解
Nginx 的 HTTP 模块是处理 HTTP 请求和响应的核心组件。根据其职责和用途,HTTP 模块可以分为多种类型。以下是常见的 HTTP 模块类型及其作用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ngx_module_t ngx_http_xxx_module = { // 模块变量名带 `http_` 前缀
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_xxx_module_ctx, // 上下文
ngx_http_xxx_commands, // 指令集
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, // 关键标记:必须是这个类型
...
};
| 大分类 | 分类说明 | 模块名称 | 作用阶段 | 功能说明 | 典型指令 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 核心基础模块 | Nginx 必备基础功能,提供 HTTP 服务核心配置 | ngx_http_core_module | 多阶段 | HTTP 基础配置(server/location 块、请求解析、变量处理) | server, listen, root |
| Handler 模块 | 生成响应内容(直接处理请求并返回数据,如静态文件、代理结果、动态程序输出) | ngx_http_static_module | NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE | 处理静态文件请求(如 HTML/图片) | root, alias |
ngx_http_proxy_module | NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE | 反向代理(转发请求到后端服务器) | proxy_pass | ||
ngx_http_fastcgi_module | NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE | 处理 FastCGI 请求(如 PHP-FPM) | fastcgi_pass | ||
| Filter 模块 | 修改响应内容(对 Handler 生成的响应进行加工,如压缩、修改 Header、日志记录) | ngx_http_headers_module | NGX_HTTP_HEADER_FILTER_PHASE | 修改响应头(如 Cache-Control、CORS) | add_header |
ngx_http_gzip_filter_module | NGX_HTTP_BODY_FILTER_PHASE | Gzip 压缩响应内容(减少传输体积) | gzip on | ||
ngx_http_log_module | NGX_HTTP_LOG_PHASE | 记录访问日志(时间、IP、状态码) | access_log | ||
| Upstream 模块 | 管理与后端服务器的交互(负载均衡、健康检查) | ngx_http_upstream_module | NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_PHASE | 定义后端服务器组(负载均衡、健康检查) | upstream, server |
| 访问控制模块 | 实现请求的访问控制(如 IP 黑白名单、鉴权) | ngx_http_access_module | NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE | 基于 IP 的访问控制(黑白名单) | allow, deny |
| SSL/TLS 模块 | 提供 HTTPS 加密支持 | ngx_http_ssl_module | NGX_HTTP_SSL_PHASE | 配置 HTTPS 证书和加密协议 | ssl_certificate |
| URL 重写模块 | 修改请求的 URL 路径(重定向、正则匹配) | ngx_http_rewrite_module | NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE | URL 重定向和重写(正则匹配) | rewrite, return |
| 第三方模块 | 扩展 Nginx 功能(需手动编译或动态加载) | ngx_http_lua_module | 多阶段 | 嵌入 Lua 脚本(动态逻辑、鉴权) | content_by_lua |
2. 过滤模块意义 ———— http 框架的11 个阶段
| 阶段(Phase) | 是否允许模块接入 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1. POST_READ | ✅ 是 | 读取请求头后立即执行,可用于全局变量初始化(如 ngx_http_realip_module)。 |
| 2. SERVER_REWRITE | ✅ 是 | 在 server 块内执行 URL 重写(如 ngx_http_rewrite_module)。 |
| 3. FIND_CONFIG | ❌ 否 | Nginx 核心阶段,决定使用哪个 location 块,模块无法干预。 |
| 4. REWRITE | ✅ 是 | 在 location 块内执行 URL 重写(如 ngx_http_rewrite_module)。 |
| 5. POST_REWRITE | ❌ 否 | 检查 REWRITE 阶段是否导致 location 变更,模块无法干预。 |
| 6. PREACCESS | ✅ 是 | 访问控制前执行(如限流 ngx_http_limit_req_module)。 |
| 7. ACCESS | ✅ 是 | 访问权限检查(如 ngx_http_access_module、ngx_http_auth_basic_module)。 |
| 8. POST_ACCESS | ❌ 否 | 检查 ACCESS 阶段结果,模块无法干预。 |
| 9. PRECONTENT | ✅ 是 | 生成内容前的最后处理(如 ngx_http_try_files_module)。 |
| 10. CONTENT | ✅ 是 | 生成响应内容(如 ngx_http_proxy_module、ngx_http_static_module)。 |
| 11. LOG | ✅ 是 | 记录访问日志(如 ngx_http_log_module)。 |
3. Nginx 中的所有模块 ? 启动顺序等
概览
- ngx_modules 中保存着所有的ngxin 编译模块
- Nginx 启动时,会按 ngx_modules[] 数组顺序依次调用每个模块的 init_module 钩子(如果定义了)。越靠前的模块越早初始化(例如核心模块 ngx_http_core_module 通常在最前面)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
~/nginx-1.0.14/objs/ngx_modules.c
ngx_module_t *ngx_modules[] = {
&ngx_core_module,
&ngx_errlog_module,
&ngx_conf_module,
&ngx_events_module,
&ngx_event_core_module,
&ngx_epoll_module,
&ngx_http_module,
&ngx_http_core_module,
&ngx_http_log_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_module,
&ngx_http_static_module,
&ngx_http_autoindex_module,
&ngx_http_index_module,
&ngx_http_auth_basic_module,
&ngx_http_access_module,
&ngx_http_limit_zone_module,
&ngx_http_limit_req_module,
&ngx_http_geo_module,
&ngx_http_map_module,
&ngx_http_split_clients_module,
&ngx_http_referer_module,
&ngx_http_rewrite_module,
&ngx_http_proxy_module,
&ngx_http_fastcgi_module,
&ngx_http_uwsgi_module,
&ngx_http_scgi_module,
&ngx_http_memcached_module,
&ngx_http_empty_gif_module,
&ngx_http_browser_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module,
&ngx_http_mytest_module,
&ngx_http_write_filter_module,
&ngx_http_header_filter_module,
&ngx_http_chunked_filter_module,
&ngx_http_range_header_filter_module,
&ngx_http_gzip_filter_module,
&ngx_http_postpone_filter_module,
&ngx_http_ssi_filter_module,
&ngx_http_charset_filter_module,
&ngx_http_userid_filter_module,
&ngx_http_headers_filter_module,
&ngx_http_copy_filter_module,
&ngx_http_range_body_filter_module,
&ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module,
NULL
};
3.1顺序说明
所有模块(核心/第三方)均按编译顺序存入 ngx_module_t *ngx_modules[] 数组,其顺序严格决定以下行为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 示例数组结构(实际由configure生成)
ngx_module_t *ngx_modules[] = {
&ngx_core_module, // 核心模块1(最先加载)
&ngx_http_core_module, // HTTP核心模块
&ngx_http_rewrite_module, // 标准HTTP模块
&my_custom_module, // 第三方模块
NULL // 数组结束
};
1. 第一定律:全局初始化顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
// nginx.c 中的初始化逻辑
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->init_module) {
ngx_modules[i]->init_module(cycle); // 绝对按数组顺序执行
}
}
做什么:内存池/全局变量等基础初始化
顺序不可变:ngx_core_module 必须第一个初始化
2. 第二定律:HTTP模块配置初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// ngx_http_block() 中的HTTP模块初始化
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) continue;
hmod = ngx_modules[i]->ctx;
if (hmod->preconfiguration) hmod->preconfiguration(cf); // 阶段1
if (hmod->postconfiguration) hmod->postconfiguration(cf); // 阶段2
}
- 顺序规则:
- 仍按 ngx_modules[] 顺序调用
- 但 preconfiguration 和 postconfiguration 是分开的两个阶段
3. 第三定律:请求处理顺序
不是所有 HTTP 模块都会完整参与 Nginx 的 11 个请求处理阶段。模块是否介入这些阶段,完全取决于它的 功能定位 和 开发者的设计意图。
| 模块类型 | 顺序规则 | 示例模块 |
|---|---|---|
| 非过滤模块 | 按11个阶段顺序执行 | ngx_http_proxy_module |
| Header Filters | 与 ngx_modules[] 顺序相同 | ngx_http_headers_filter_module |
| Body Filters | 与 ngx_modules[] 顺序相反 | ngx_http_gzip_filter_module |
3.2再谈配置解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_mytest_module_ctx =
{
NULL, /* preconfiguration */
NULL, /* postconfiguration */
NULL, /* create main configuration */
NULL, /* init main configuration */
NULL, /* create server configuration */
NULL, /* merge server configuration */
NULL, /* create location configuration */
NULL /* merge location configuration */
};
调用每个模块的 create xxx configuration && preconfiguration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
// 当解析到http{}块时执行的伪代码(ngx_http_block函数简化版)
void ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf) {
// 阶段1:调用所有HTTP模块的preconfiguration
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) continue;
hmod = ngx_modules[i]->ctx;
if (hmod->preconfiguration) {
hmod->preconfiguration(cf); // 此时尚未创建任何配置结构
}
}
// 阶段2:创建配置结构(MAIN/SRV/LOC)
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) continue;
hmod = ngx_modules[i]->ctx;
if (hmod->create_main_conf) {
ctx->main_conf[mi] = hmod->create_main_conf(cf);
}
if (hmod->create_srv_conf) {
ctx->srv_conf[mi] = hmod->create_srv_conf(cf);
}
if (hmod->create_loc_conf) {
ctx->loc_conf[mi] = hmod->create_loc_conf(cf);
}
}
// 阶段3:解析server{}和location{}配置
parse_servers_and_locations(cf);
// 阶段4:调用所有HTTP模块的postconfiguration
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) continue;
hmod = ngx_modules[i]->ctx;
if (hmod->postconfiguration) {
hmod->postconfiguration(cf); // 此时所有配置已就绪
}
}
}
preconfiguration & postconfiguration | 特性 | preconfiguration | postconfiguration | |———————|——————————————|——————————————| | 调用阶段 | 刚进入http{}块,尚未解析任何server/location | 已完成http{}内所有server/location的解析 | | 典型用途 | 早期全局初始化 | 注册处理程序/过滤器 | | 执行顺序 | 按ngx_modules[]数组顺序 | 按ngx_modules[]数组顺序 | | 可否访问配置 | ❌ 配置未生成 | ✅ 可读取main/srv/loc配置 | | 官方模块使用案例 | ngx_http_realip_module | ngx_http_gzip_filter_module |
ngxin中的过滤模块顺序
| 模块名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module | 仅对 HTTP 头部做处理。在返回 200 成功时,根据请求中的 If-Modified-Since 或 If-Unmodified-Since 头部获取浏览器缓存文件的最后修改时间,决定是否直接发送 304 Not Modified 响应给用户。 |
ngx_http_range_header_filter_module | 处理请求中的 Range 信息,根据 Range 中的要求返回文件的一部分给用户。 |
ngx_http_copy_filter_module | 仅对 HTTP 包体做处理。将用户发送的 ngx_chain_t 结构的 HTTP 包体复制到新的 ngx_chain_t 结构中(仅复制指针,不包括实际 HTTP 响应内容),后续的 HTTP 过滤模块处理的 ngx_chain_t 类型的成员都是该模块处理后的变量。 |
ngx_http_headers_filter_module | 仅对 HTTP 头部做处理。允许通过配置文件在响应中添加任意的 HTTP 头部。 |
ngx_http_userid_filter_module | 基于 Cookie 提供简单的认证管理功能。 |
ngx_http_charset_filter_module | 仅对 HTTP 包体做处理。将响应包按照配置文件中的配置重新编码后返回给用户。 |
ngx_http_ssi_filter_module | 仅对 HTTP 包体做处理。支持 SSI(Server Side Include),将文件内容嵌入到网页中并返回给用户。 |
ngx_http_postpone_filter_module | 处理子请求的响应,确保多个子请求的响应按顺序发送。 |
ngx_http_gzip_filter_module | 仅对 HTTP 包体做处理。对特定的 HTTP 响应包体(如网页或文本文件)进行 Gzip 压缩后返回给用户。 |
ngx_http_range_filter_module | 支持 Range 协议。 |
ngx_http_chunked_filter_module | 支持 chunked 编码。 |
ngx_http_header_filter_module | 将响应头部序列化为字符流,并通过 ngx_http_write_filter_module 发送到客户端。 |
ngx_http_write_filter_module | 负责向客户端发送 HTTP 响应包体。 |
第三方过滤模块执行顺序
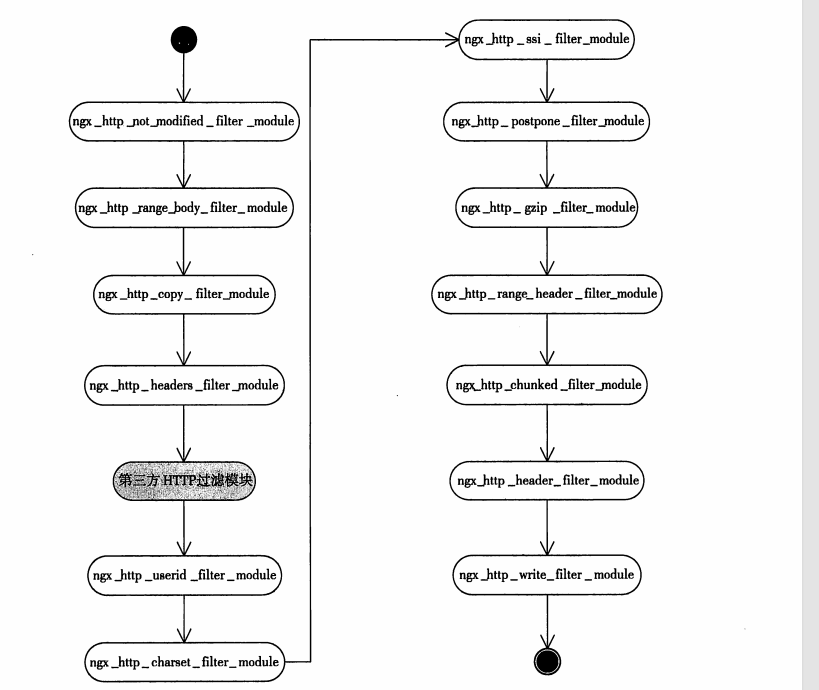
3. Http 模块 和 Http Filter 模块区别?
1
2
// config
HTTP_FILTER_MODULES="$HTTP_FILTER_MODULES ngx_http_myfilter_module"
还有的一些http 模块:
- ngx_http_ssl_module
- ngx_http_upstream_module
- 等
4. Nginx filter 模块示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#include <ngx_http.h>
typedef struct
{
ngx_flag_t enable;
} ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t;
typedef struct
{
ngx_int_t add_prefix;
} ngx_http_myfilter_ctx_t;
static ngx_http_output_header_filter_pt ngx_http_next_header_filter;
static ngx_http_output_body_filter_pt ngx_http_next_body_filter;
//将在包体中添加这个前缀
static ngx_str_t filter_prefix = ngx_string("[my filter prefix]");
static void* ngx_http_myfilter_create_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf);
static char *
ngx_http_myfilter_merge_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child);
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_myfilter_init(ngx_conf_t *cf);
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_myfilter_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r);
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_myfilter_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in);
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_myfilter_commands[] =
{
{
ngx_string("add_prefix"),
NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF | NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF | NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF | NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF | NGX_CONF_FLAG,
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t, enable),
NULL
},
ngx_null_command
};
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_myfilter_module_ctx =
{
NULL, /* preconfiguration方法 */
ngx_http_myfilter_init, /* postconfiguration方法 */
NULL, /*create_main_conf 方法 */
NULL, /* init_main_conf方法 */
NULL, /* create_srv_conf方法 */
NULL, /* merge_srv_conf方法 */
ngx_http_myfilter_create_conf, /* create_loc_conf方法 */
ngx_http_myfilter_merge_conf /*merge_loc_conf方法*/
};
ngx_module_t ngx_http_myfilter_module =
{
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_myfilter_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_http_myfilter_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_myfilter_init(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
//插入到头部处理方法链表的首部
ngx_http_next_header_filter = ngx_http_top_header_filter;
ngx_http_top_header_filter = ngx_http_myfilter_header_filter;
//插入到包体处理方法链表的首部
ngx_http_next_body_filter = ngx_http_top_body_filter;
ngx_http_top_body_filter = ngx_http_myfilter_body_filter;
return NGX_OK;
}
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_myfilter_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
ngx_http_myfilter_ctx_t *ctx;
ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t *conf;
//如果不是返回成功,这时是不需要理会是否加前缀的,直接交由下一个过滤模块
//处理响应码非200的情形
if (r->headers_out.status != NGX_HTTP_OK)
{
return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
}
//获取http上下文
ctx = ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, ngx_http_myfilter_module);
if (ctx)
{
//该请求的上下文已经存在,这说明
// ngx_http_myfilter_header_filter已经被调用过1次,
//直接交由下一个过滤模块处理
return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
}
//获取存储配置项的ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t结构体
conf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_myfilter_module);
//如果enable成员为0,也就是配置文件中没有配置add_prefix配置项,
//或者add_prefix配置项的参数值是off,这时直接交由下一个过滤模块处理
if (conf->enable == 0)
{
return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
}
//构造http上下文结构体ngx_http_myfilter_ctx_t
ctx = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_myfilter_ctx_t));
if (ctx == NULL)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
//add_prefix为0表示不加前缀
ctx->add_prefix = 0;
//将构造的上下文设置到当前请求中
ngx_http_set_ctx(r, ctx, ngx_http_myfilter_module);
//myfilter过滤模块只处理Content-Type是"text/plain"类型的http响应
if (r->headers_out.content_type.len >= sizeof("text/plain") - 1
&& ngx_strncasecmp(r->headers_out.content_type.data, (u_char *) "text/plain", sizeof("text/plain") - 1) == 0)
{
//1表示需要在http包体前加入前缀
ctx->add_prefix = 1;
//如果处理模块已经在Content-Length写入了http包体的长度,由于
//我们加入了前缀字符串,所以需要把这个字符串的长度也加入到
//Content-Length中
if (r->headers_out.content_length_n > 0)
r->headers_out.content_length_n += filter_prefix.len;
}
//交由下一个过滤模块继续处理
return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
}
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_myfilter_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in)
{
ngx_http_myfilter_ctx_t *ctx;
ctx = ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, ngx_http_myfilter_module);
//如果获取不到上下文,或者上下文结构体中的add_prefix为0或者2时,
//都不会添加前缀,这时直接交给下一个http过滤模块处理
if (ctx == NULL || ctx->add_prefix != 1)
{
return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in);
}
//将add_prefix设置为2,这样即使ngx_http_myfilter_body_filter
//再次回调时,也不会重复添加前缀
ctx->add_prefix = 2;
//从请求的内存池中分配内存,用于存储字符串前缀
ngx_buf_t* b = ngx_create_temp_buf(r->pool, filter_prefix.len);
//将ngx_buf_t中的指针正确地指向filter_prefix字符串
b->start = b->pos = filter_prefix.data;
b->last = b->pos + filter_prefix.len;
//从请求的内存池中生成ngx_chain_t链表,将刚分配的ngx_buf_t设置到
//其buf成员中,并将它添加到原先待发送的http包体前面
ngx_chain_t *cl = ngx_alloc_chain_link(r->pool);
cl->buf = b;
cl->next = in;
//调用下一个模块的http包体处理方法,注意这时传入的是新生成的cl链表
return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, cl);
}
static void* ngx_http_myfilter_create_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t *mycf;
//创建存储配置项的结构体
mycf = (ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t *)ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t));
if (mycf == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//ngx_flat_t类型的变量,如果使用预设函数ngx_conf_set_flag_slot
//解析配置项参数,必须初始化为NGX_CONF_UNSET
mycf->enable = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
return mycf;
}
static char *
ngx_http_myfilter_merge_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child)
{
ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t *prev = (ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t *)parent;
ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t *conf = (ngx_http_myfilter_conf_t *)child;
//合并ngx_flat_t类型的配置项enable
ngx_conf_merge_value(conf->enable, prev->enable, 0);
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
